
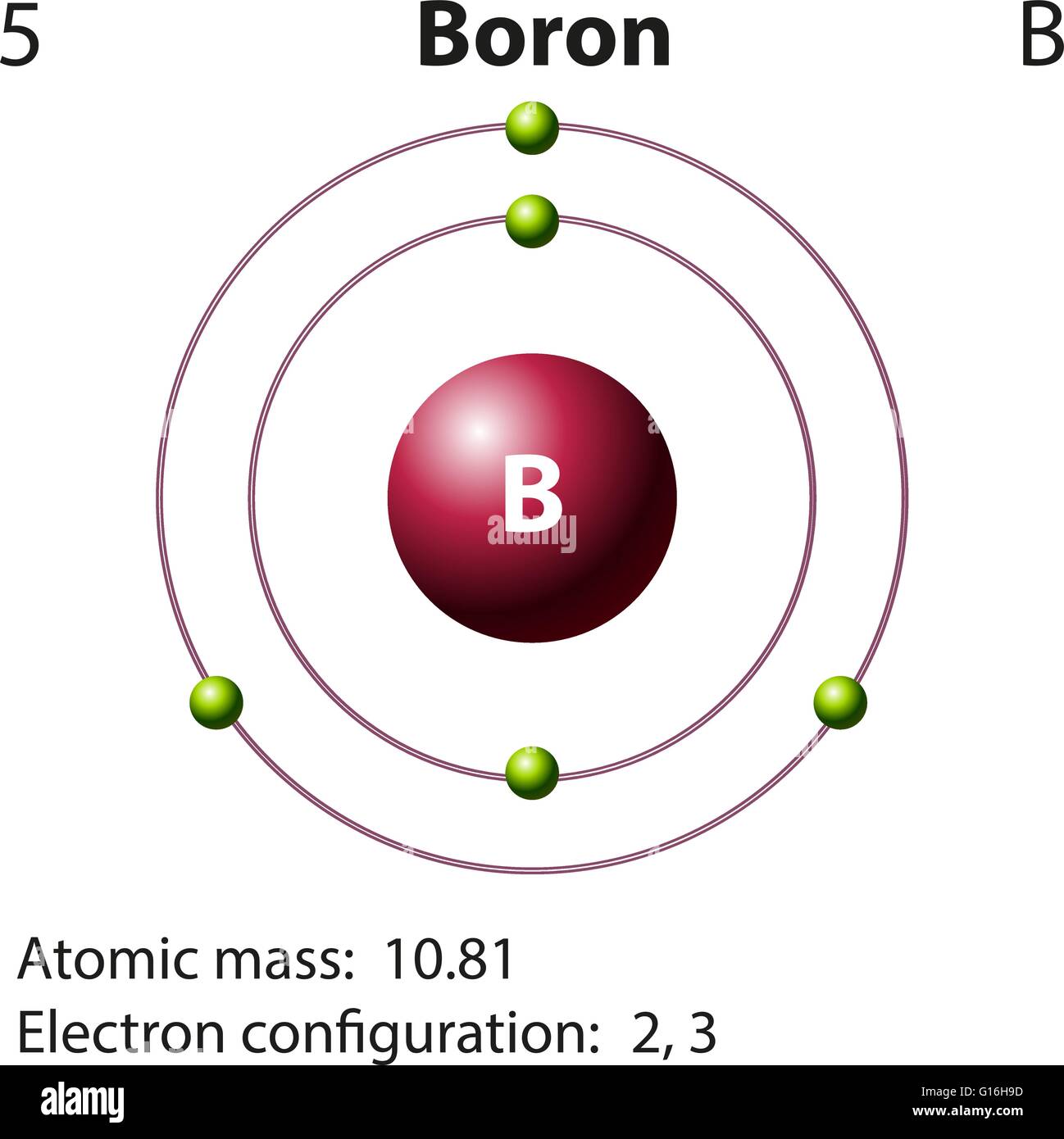
Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z.
Other boron compounds are used in a variety of things, for example: adhesives, cement, disinfectants, fertilizers, fire retardants, glass, herbicides, metallurgical fluxes, and textile bleaches and dye.Atomic Number – Protons, Electrons and Neutrons in Boronīoron is a chemical element with atomic number 5 which means there are 5 protons in its nucleus. Boric acid is also used as an insecticide to kill roaches, and as an antiseptic in eyewash solutions. When mixed with water, the weakly acidic and electron deficient boric acid accepts an OH- ion from water and forms the complex ion -.īorate salts produce basic solutions that are used in cleaning agents. Another compound that other boron compounds can be synthesized from is boric acid (B(OH) 3). The key to the bleaching ability of this compound is the presence of its two peroxo groups that bridge the boron atoms together. Sodium perborate is used in color-safe bleaches. When a solution of borax and hydrogen peroxide is crystallized, sodium perborate (NaBO 3 * 4 H 2O) is formed. Borax is the most common ore found, and it can be turned into a variety of boron compounds. The bond between the H and the B atoms can be rationalized using molecular orbital theory.Īlthough boron compounds are widely distributed in Earth's crust, a few concentrated ores are located in Italy, Russia, Tibet, Turkey, and California. These bonds are also called three-center two-electron bonds. This creates what is called an atom "bridge" because there are two electrons shared among three atoms. This is done when the two H atoms simultaneously bond to the two B atoms. Four electrons bond the remaining H atoms to the two B atoms and the B atoms together. In these four bonds 8 electrons are involved. According to this figure, the two B atoms and four H atoms lie in the same plane (sp 3- perpendicular to the plane of the page).
To make this structure follow the rules required to draw any lewis structure model, then it must have 14 valence shell electrons however it does not. This molecule has 12 valence shell electrons 3 each from the B atoms, and 1 each from the six H atoms. The boron atom has only six electrons in its outer shell, leading to an electron deficiency. In the molecule BH 3, each of the 3 hydrogen atoms is bonded to the central boron atom.

Boron-hydrogen compounds are referred to as boron hydrides, or boranes. This deficiency is what accounts for boron being a strong Lewis acid, in that it can accept protons (H + ions) in solution. Many boron compounds are electron-deficient, meaning that they lack an octet of electrons around the central boron atom. Chemically, it is closer to aluminum than any of the other group 13 elements. For example Boron is a semiconductor unlike the rest of the group 13 elements. It has properties that lie between metals and non-metals (semimetals). Atomic Massīoron is the only element in group 3 that is not a metal. Common compounds of boron include borax and boric acid (\(H_3BO_3\)). High-purity boron can be produced by electrolysis of molten potassium fluoroborate. The element can be prepared by the reduction of borax (\(Na_2B_4O_7\)) with carbon. In addition to the crystalline form of boron there is also an amorphous dark brown powder (as shown above). This behavior as well as many of its other properties earn it the classification of a metalloid. At high temperatures it is a good conductor but at room temperature and below is an insulator. It is very hard and in extremely pure form is nearly as hard as diamond, but much too brittle for practical use. Although compounds of boron were known in ancient times, it was first isolated in 1808 by Gay-Lussac and Thénard and independently by Sir Humphry Davy (who has a lot of elements to his credit!).īoron exists in the earth's crust to the extent of only about 10 ppm (about the same abundance as lead). The name Boron comes from the Arabic and Persian words for borax, its principal ore.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
